How to navigate risks in the digital age
This article digs into effective strategies to manage risks in the digital era, highlighting the pivotal role of technology intelligence in navigating risks within R&D sectors, especially within the life sciences realm of billion-dollar manufacturers.
This article was written in collaboration with the Valona Intelligence Community. Members exchange knowledge, insights, and best practices across the globe.
Watch the webinar that sparked this discussion, ‘Supercharging Risk Management with MI’.
The core tenets of risk management
Gone are the days when risk management was viewed solely through the lens of compliance. Organizations must adopt a mindset that encompasses both risk and threat. This means recognizing that regulations are not just checkboxes to tick off but integral components of the risk landscape.
By acknowledging the evolving nature of cyber threats and embracing a proactive approach to risk management, businesses can better safeguard their operations and reputation.
At the heart of effective risk management lie four fundamental pillars:
Identify, assess, respond, and monitor

Organizations must proactively identify potential risks and threats, assess their potential impact, and develop tailored responses to mitigate or address them.
Continuous monitoring and reporting ensure that risk management remains an ongoing and iterative process, enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Integrating AI and cybersecurity into risk management
As organizations increasingly rely on AI and digital technologies, the integration of cybersecurity into risk management practices becomes paramount. This involves conducting comprehensive assessments of cyber capabilities, designing robust strategies and programs, and implementing stringent risk governance and oversight measures.
Additionally, responsible AI practices, including ethics, fairness, and security considerations, are critical for ensuring the integrity and reliability of AI-driven systems.
Navigating risks in R&D
Pillars of risk management: technology and intelligence strategies
In our exploration of managing risks within R&D investments and market growth, we pivot towards the realm of technology intelligence.
Here, we delve into the pillars guiding our approach, emphasizing a nuanced understanding of audience needs and the timely dissemination of actionable insights. After all, informed decision-making is the cornerstone of effective risk management.
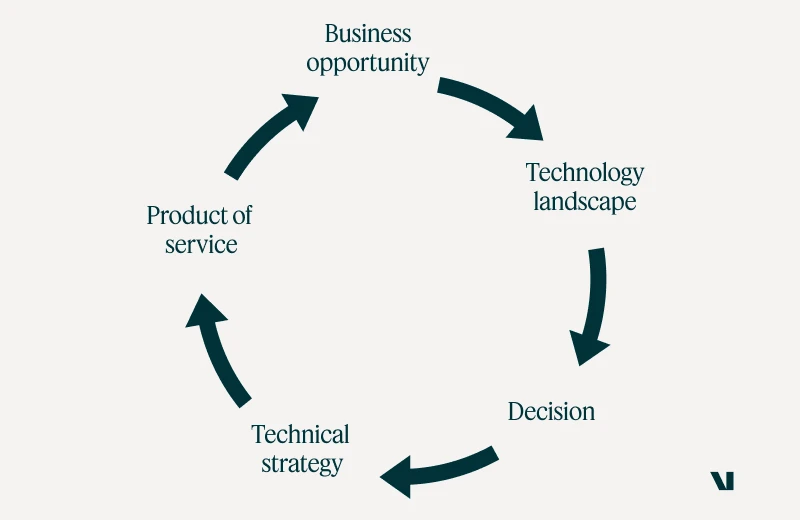
Diverse sources, informed decisions: the arsenal of technology intelligence
In this dynamic landscape, our reliance on diverse sources of technological intelligence becomes apparent. From patent publications to venture capital investments, we cast a wide net to capture the pulse of innovation. By synthesizing these insights, we empower decision-makers to chart a course that aligns with our organizational goals and market realities.
Learning from real-world use cases
Examining real-world use cases provides valuable insights into the impact of cyber threats on organizations. From the SolarWinds breach affecting thousands of customers to the ransomware attacks targeting major corporations like CNA Financial and MGM Resorts, these incidents underscore the importance of robust risk management practices.
By learning from such experiences and implementing proactive measures, organizations can mitigate the potential fallout of cyber-attacks and protect sensitive data.
Case study: navigating risks in the alternative meat industry
In this landscape, a billion-dollar revenue life science manufacturer needed to assess the regional nuances of consumer preferences and regulatory frameworks, balancing short-term market demands with long-term technological investments.
This sector, characterized by its disruptive potential and multifaceted challenges, serves as a microcosm of the complexities inherent in innovation-driven markets.
Within the alternative meat industry, various subcategories emerge, including plant-based meats, high-protein alternatives, and cellular agriculture. Each presents unique opportunities and challenges, from personal health and sustainability to regulatory approval and consumer acceptance.
Whether it’s partnering with universities to explore emerging technologies or tracking venture capital investments for market insights, their approach to technology intelligence informs strategic decision-making in the alternative meat sector.
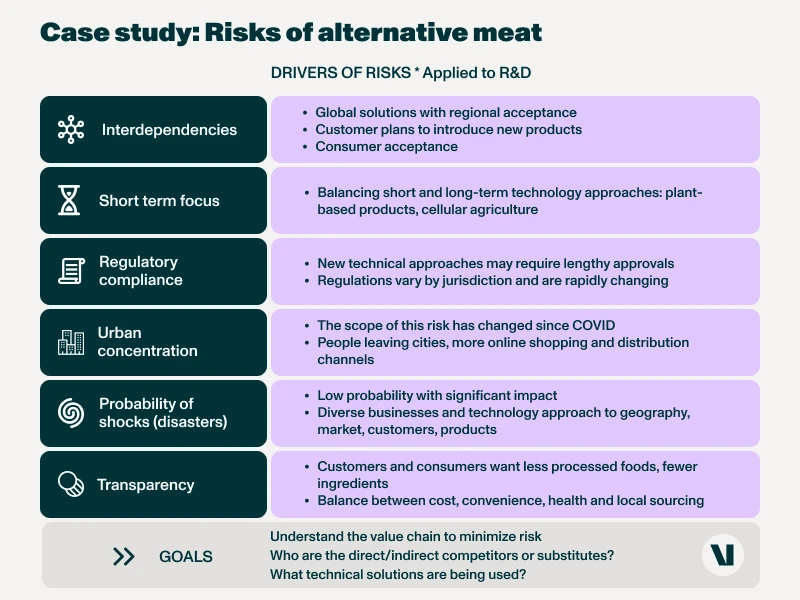
A comprehensive approach to risk management
In conclusion, effective risk management is no longer optional—it’s a business imperative.
It requires a proactive approach and integration of AI, cybersecurity, and real-world insights in the digital age. By adopting comprehensive strategies, organizations can mitigate threats and thrive in this rapidly evolving landscape. Furthermore, proactive risk management safeguards operations and fosters trust with stakeholders.
Technology intelligence isn’t just about staying ahead—it’s about shaping the future. Through strategic foresight and informed action, we can unlock the potential of innovation and navigate risks with confidence. In the realm of R&D, knowledge truly is power.
Additional insights from discussions with CI/MI experts at the Valona Intelligence Community’s Roundtables:
- Trust tracking challenges: Despite the importance of trust and confidence in business, tracking these metrics remains elusive. Edelman’s trust barometer offers a starting point, but deeper insights are needed.
- Tech strategy as a priority: It has implications across industries, and understanding its trajectory is key to staying competitive.
- Collaborative insights: Inter-team collaboration is essential for gaining comprehensive insights. Regular meetings facilitate connecting the dots and identifying emerging trends.
- From hindsight to foresight: Competitive intelligence professionals are shifting from reactive to proactive approaches. Predictive intelligence and scenario planning enable anticipating future risks and opportunities.
- Data management challenges: Effectively managing and analyzing vast amounts of data presents hurdles. Leveraging tools like AI, market research platforms, and strategic partnerships is crucial for success.
An impact beyond data analysis
In MI, the advent of AI has enhanced data access and analysis. AI facilitates quick access to real-time information, offering insights into industry trends and competitive landscapes.
Moreover, AI tools streamline data summarization and analysis, alleviating the burden of manual data sifting and enabling deeper insights into market dynamics. Despite AI’s capabilities, strategic decision-making remains deeply rooted in human judgment.
While AI augments data accessibility and analysis, the significance of human oversight in selecting and curating data cannot be overstated.
AI’s impact extends beyond mere data analysis—it fosters a cultural shift towards insight-driven decision-making within organizations. This shift emphasizes collaboration and elevates decision quality across departments.
Are you interested in joining live conversations about the most pertinent topics in MI and CI?
Join our upcoming events! They are regularly scheduled, professionally facilitated roundtables and discussions.




